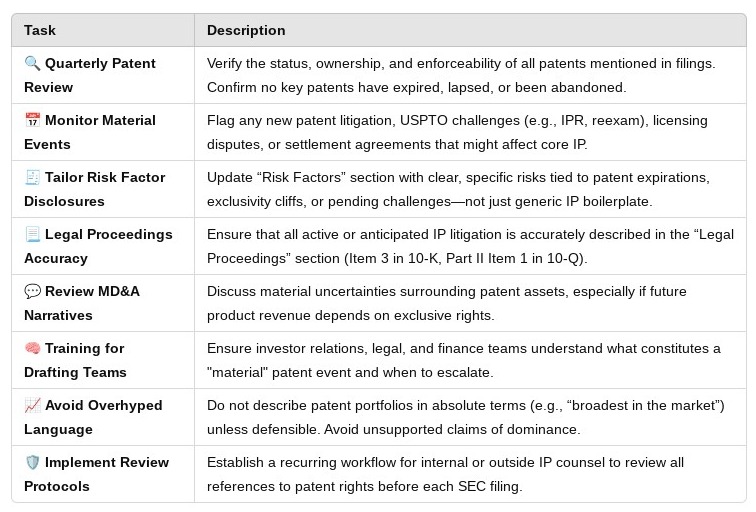
How to Secure Patents – Checklist
Securing Patents Under U.C.C. Article 9 and USPTO Rules
🔒 For Lenders: Ensuring a Perfected and Enforceable Security Interest
🔁 Pre-Closing Diligence
-
☐ Confirm patent ownership via USPTO Assignment Search
-
☐ Identify all relevant patents and patent applications, including continuations/divisionals
-
☐ Ensure debtor (borrower) has rights in the collateral
-
☐ Confirm there are no existing liens or licenses that impair enforceability or priority
✍️ Security Agreement
-
☐ Clearly describe collateral, including:
-
All issued patents
-
Patent applications
-
Proceeds, royalties, and income streams
-
-
☐ Include a schedule of patents with registration numbers
-
☐ Require borrower to maintain patents and pay USPTO fees
-
☐ Include covenants about:
-
Not abandoning patents
-
Reporting infringement or litigation
-
Not transferring ownership without lender consent
-
📁 Perfection Under Article 9
-
☐ File U.C.C.-1 financing statement in debtor’s state of incorporation
-
☐ Use precise legal name of debtor (check Secretary of State records)
-
☐ Use broad, but accurate, collateral language (e.g., “All general intangibles including patents and proceeds”)
🏛️ Recordation with the USPTO
-
☐ Prepare and file a confirmatory security agreement
-
☐ File via USPTO Assignment Recordation Portal
-
☐ Double-check:
-
Patent numbers are correct
-
Debtor/secured party names match U.C.C. filing
-
Agreement language identifies the interest as a security interest
-
🔍 Ongoing Monitoring
-
☐ Periodically review:
-
Assignment records at USPTO
-
U.C.C. financing statement status
-
Maintenance fee payments
-
-
☐ Include renewal or continuation of U.C.C. filing (5-year limit)
-
☐ Track encumbrances, litigation, and ownership changes
🧾 For Borrowers: Staying Compliant and Protecting Your Assets
🧱 Internal Records and Ownership
-
☐ Maintain internal IP ledger with:
-
Patent numbers
-
Application status
-
Dates of issuance and expiration
-
-
☐ Ensure all patents are properly assigned to the borrowing entity
-
☐ Disclose:
-
Pending applications
-
Joint ownership
-
Prior licenses or encumbrances
-
🤝 During Negotiation
-
☐ Carefully review the security agreement for:
-
Scope of rights being pledged
-
Borrower obligations
-
Cure periods and default triggers
-
-
☐ Retain copies of all signed documents and filings
📣 Post-Closing Obligations
-
☐ Monitor and pay USPTO maintenance fees on time
-
☐ Notify lender promptly of:
-
Patent litigation or challenges
-
Office actions or reexaminations
-
Material changes to title or scope of rights
-
-
☐ Provide lender with:
-
Updated patent schedules annually
-
Notices of license agreements or transfers
-
🧯 In Case of Default
-
☐ Understand lender’s rights to:
-
Foreclose on or transfer patents
-
License, sell, or monetize rights
-
-
☐ Be prepared to cooperate in IP asset recovery or enforcement proceedings
Additional Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua